Exploring the intricate relationship between sleep and long-term brain health unveils a fascinating journey into the inner workings of our most vital organ. From the restorative functions of sleep to the detrimental effects of sleep deprivation, this topic delves into the core of how our nightly rest impacts our cognitive well-being.
Delving deeper into the effects of sleep on brain health, we uncover a wealth of information that sheds light on the importance of quality rest for optimal brain function.
The Importance of Sleep for Brain Health
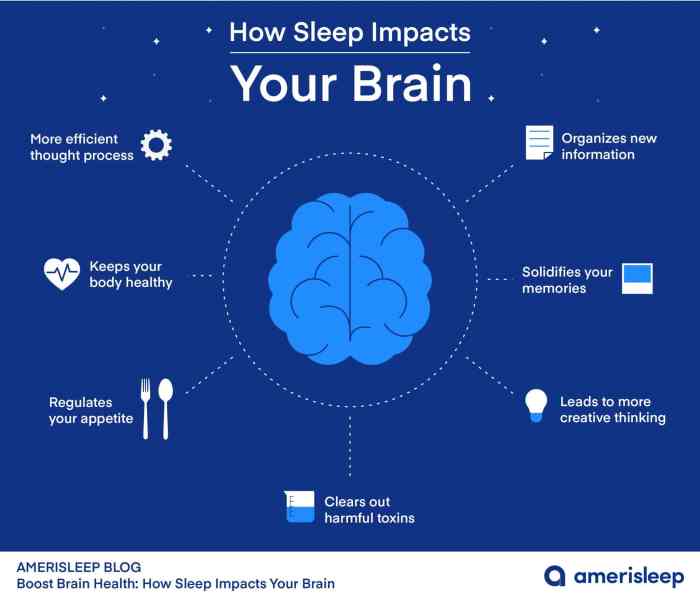
Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining long-term brain health. It is during sleep that the brain undergoes essential processes to repair and consolidate memories, regulate emotions, and clear out toxins that accumulate throughout the day.
Impact of Inadequate Sleep on Brain Function
- Impaired cognitive function: Lack of sleep can lead to difficulties with concentration, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- Memory problems: Inadequate sleep can hinder the brain's ability to form and retain memories, affecting learning and overall cognitive performance.
- Emotional disturbances: Sleep deprivation can contribute to mood swings, irritability, and heightened emotional reactivity.
Role of Different Stages of Sleep in Brain Health
- NREM (Non-Rapid Eye Movement) Sleep: This stage is crucial for memory consolidation, learning, and overall cognitive function.
- REM (Rapid Eye Movement) Sleep: REM sleep is essential for emotional regulation, creativity, and problem-solving abilities.
- Deep Sleep: Also known as slow-wave sleep, this stage is essential for physical restoration, hormone regulation, and overall brain detoxification.
Effects of Sleep Deprivation on the Brain
Sleep deprivation can have serious consequences on brain health, impacting cognitive functions, memory, learning, and increasing the risk of neurological disorders.
Impact on Cognitive Functions
- Chronic sleep deprivation can impair attention, decision-making, problem-solving, and creativity.
- It can lead to decreased cognitive flexibility, slower reaction times, and poor judgment.
- Individuals may experience difficulty in concentrating, multitasking, and retaining information.
Impact on Memory and Learning
- Sleep deprivation disrupts the consolidation of memories, affecting the ability to form and retain new information.
- It impairs the process of memory recall, making it challenging to retrieve stored information when needed.
- Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to a decline in academic performance and cognitive skills.
Relationship with Neurological Disorders
- Prolonged sleep deprivation is associated with an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
- It can exacerbate symptoms of existing neurological disorders and worsen cognitive decline over time.
- Research suggests that inadequate sleep may contribute to the development of conditions such as dementia and cognitive impairment.
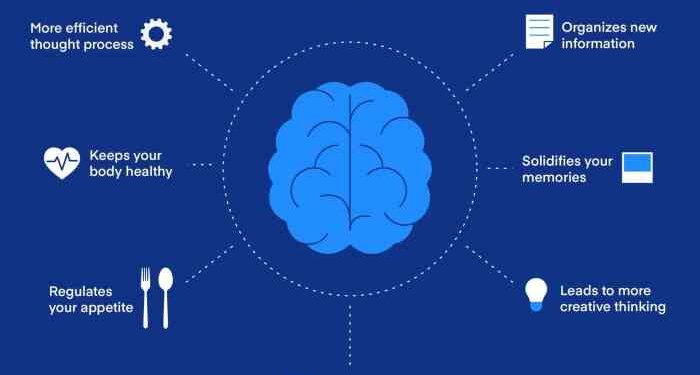
Restorative Functions of Sleep for Brain Health
Sleep plays a crucial role in the restorative functions of brain health. It is during sleep that the brain undergoes essential processes to repair, maintain, and optimize its functions.
Facilitating Repair and Maintenance of Brain Cells
During sleep, the brain engages in various repair mechanisms to ensure the optimal functioning of brain cells
Consolidating Memories and Knowledge
One of the key functions of sleep is to consolidate memories and knowledge acquired throughout the day. During sleep, the brain processes and stores information gathered during wakefulness, strengthening connections between neurons and enhancing memory retention. This process is crucial for learning and cognitive function.
Clearing Toxins and Waste Products from the Brain
Sleep plays a vital role in clearing toxins and waste products from the brain. The glymphatic system, a waste clearance system in the brain, is most active during sleep. This system helps to flush out harmful substances such as beta-amyloid, a protein associated with Alzheimer's disease.
Adequate sleep is essential for the proper functioning of the glymphatic system and the removal of toxins that can impair brain health.
Impact of Sleep Disorders on Brain Health
Sleep disorders can have a significant impact on long-term brain health, affecting cognitive function, memory, and overall well-being. Common sleep disorders such as insomnia and sleep apnea can disrupt the brain's ability to rest and recharge properly, leading to a range of negative consequences.
Insomnia
Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, resulting in poor quality sleep. This can lead to cognitive impairment, decreased concentration, and memory problems. The lack of restorative sleep can affect the brain's ability to consolidate memories and process information efficiently.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, leading to oxygen deprivation and fragmented sleep. This can impact brain health by causing daytime sleepiness, poor focus, and memory issues. The disruption in oxygen flow can also increase the risk of developing conditions like hypertension and cardiovascular disease, further affecting brain function.
Treatment Options
Treatment for sleep disorders typically involves lifestyle changes, therapy, or medication, depending on the underlying cause. For insomnia, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help improve sleep habits and reduce anxiety related to sleep. Sleep apnea may require the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines to maintain proper airflow during sleep.
It is essential to address sleep disorders promptly to promote brain health and overall well-being.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding how sleep affects long-term brain health opens up a world of possibilities for enhancing our cognitive abilities and overall well-being. By prioritizing healthy sleep habits, we pave the way for a sharper mind and a healthier brain in the long run.
Key Questions Answered
How does sleep quality impact long-term brain health?
Sleep quality plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal brain function over time. Poor sleep habits can lead to cognitive decline and increase the risk of neurological disorders.
Can chronic sleep deprivation cause permanent damage to the brain?
Yes, chronic sleep deprivation can result in long-lasting cognitive impairments and affect memory consolidation and learning abilities.
What are some common sleep disorders that can affect brain health?
Conditions like insomnia, sleep apnea, and narcolepsy can have detrimental effects on long-term brain health if left untreated.